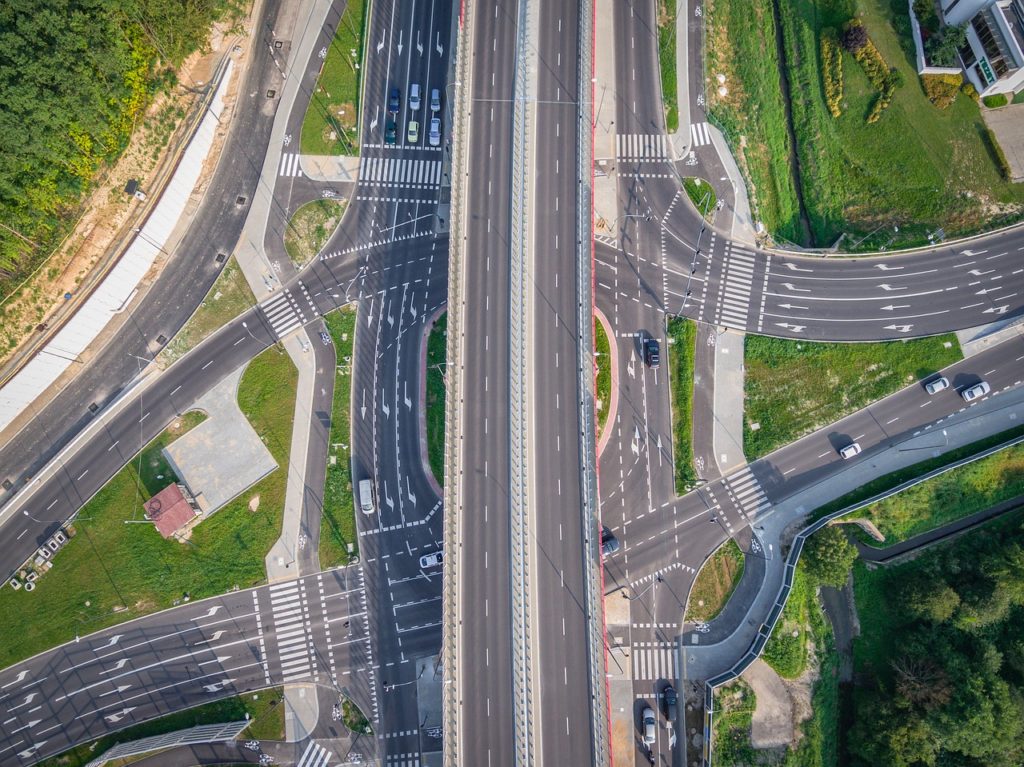
The Role of Public-Private Partnerships in Infrastructure Development
Infrastructure development is a crucial aspect of any economy, as it helps to facilitate economic growth and development. Infrastructure includes a wide range of physical structures, such as roads, bridges, ports, airports, railways, and public utilities like water and electricity. However, building and maintaining such infrastructure requires substantial investment, which can often be challenging for governments to finance on their own. This is where Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) come in.
A. Definition of Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) refer to a collaborative arrangement between a government or a public agency and a private entity, with the goal of providing a public service or developing public infrastructure. PPPs are typically long-term agreements, which involve the private sector investing in and managing the construction, operation, and maintenance of public infrastructure or services.
B. Brief explanation of infrastructure development and its importance
Infrastructure development plays a critical role in driving economic growth, creating jobs, and improving living standards. It helps to increase productivity by providing better access to markets, reducing transportation costs, and promoting innovation. For instance, efficient transportation infrastructure reduces the cost of goods and services, making them more affordable and accessible to consumers. In addition, the availability of reliable infrastructure attracts businesses, which in turn creates job opportunities and generates revenue for the government.
However, infrastructure development can be expensive, and governments often face constraints in financing such projects. This is where PPPs come in, as they allow governments to leverage private sector investment and expertise to deliver public infrastructure more efficiently and cost-effectively.
The Benefits of PPPs in Infrastructure Development
PPPs offer several benefits over traditional procurement methods for infrastructure development. Here are five key advantages of PPPs:
A. Increased Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
PPPs can lead to improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness in infrastructure development, as private sector partners are incentivized to deliver projects on time and within budget. This is because they are often contractually obligated to deliver projects to certain standards and performance metrics. Private sector partners also bring their expertise in project management, construction, and maintenance, which can help to improve project delivery and reduce costs.
B. Transfer of Risk
PPPs can also help to transfer risk from the government to the private sector. In traditional procurement methods, governments bear the full risk of a project, including cost overruns and delays. In PPPs, private sector partners share some of the risks, which incentivizes them to manage the risks and deliver projects on time and within budget. This helps to mitigate the risk of project failure and reduces the financial burden on the government.
C. Innovation and Technology
PPPs can also drive innovation and technology in infrastructure development. Private sector partners bring their knowledge and expertise in project management, construction, and maintenance, which can help to improve project delivery and reduce costs. In addition, private sector partners are often more willing to invest in new technologies and innovative solutions, which can lead to better outcomes for the government and the public.
D. Access to Financing
PPPs can provide access to financing for infrastructure development, which can be challenging for governments to obtain on their own. Private sector partners can bring their own capital and access to debt markets, which can help to finance large infrastructure projects. This can also help to reduce the burden on taxpayers, as private sector partners are often willing to finance the upfront costs of a project in exchange for a long-term revenue stream.
E. Increased Accountability and Transparency
PPPs can also increase accountability and transparency in infrastructure development. Private sector partners are contractually obligated to deliver projects to certain standards and performance metrics, which can help to ensure that projects are delivered on time and within budget. In addition, PPP contracts are typically subject to public scrutiny, which can help to increase transparency and accountability in project delivery. This can help to build public trust and confidence in the government’s ability to deliver infrastructure projects.
Examples of Successful PPPs in Infrastructure Development
PPPs have been used successfully in infrastructure development projects all over the world. Here are three examples of successful PPPs:
A. The Channel Tunnel (UK-France)
The Channel Tunnel, also known as the Eurotunnel, is a 50-kilometer-long rail tunnel that connects the United Kingdom and France. The project was completed in 1994 and is one of the most iconic PPPs in the world. The project was financed through a consortium of private investors, including several major banks, and was completed on time and within budget. The Channel Tunnel has since become an important transportation link between the UK and Europe, carrying millions of passengers and freight each year.
B. The Dulles Greenway (USA)
The Dulles Greenway is a 22-kilometer-long toll road that connects Dulles International Airport to Leesburg, Virginia. The project was completed in 1995 and was the first privately financed toll road in the United States. The project was financed through a consortium of private investors and was completed on time and within budget. The Dulles Greenway has since become an important transportation link in Northern Virginia, providing faster and more reliable access to Dulles International Airport.
C. The Sydney Desalination Plant (Australia)
The Sydney Desalination Plant is a large-scale seawater desalination plant that supplies water to Sydney, Australia. The project was completed in 2010 and is one of the largest PPPs in Australia. The project was financed through a consortium of private investors and was completed on time and within budget. The Sydney Desalination Plant has since become an important source of water for Sydney, helping to address water shortages during periods of drought.
These three examples demonstrate the potential of PPPs to deliver infrastructure projects on time and within budget, while also leveraging private sector expertise and financing to achieve better outcomes for the public.
The Challenges of PPPs in Infrastructure Development
While PPPs offer several benefits over traditional procurement methods, they also come with their own set of challenges. Here are four key challenges of PPPs:
A. Political and Legal Risks
PPPs can be subject to political and legal risks, as they involve a partnership between the government and private sector partners. Political risks include changes in government policy, which can impact the viability of a project. Legal risks include contractual disputes between the government and private sector partners, which can delay project delivery and increase costs.
B. Complex Contract Negotiations
PPPs involve complex contract negotiations between the government and private sector partners. These negotiations can be time-consuming and expensive, as they require detailed legal and financial analysis. In addition, the contracts must be carefully structured to allocate risks and rewards between the parties, which can be challenging to achieve.
C. Limited Participation by Small Firms
PPPs can also limit the participation of small firms in infrastructure development projects, as they often require significant financial and technical expertise. This can lead to a concentration of power in the hands of a few large firms, which can reduce competition and lead to higher costs for the government and the public.
D. Financing Challenges
PPPs can also face financing challenges, as they require significant upfront investment. Private sector partners may be unwilling or unable to finance the entire project, which can require the government to provide financing or guarantees. In addition, PPPs may face challenges in accessing financing, particularly in developing countries where capital markets may be less developed.
Despite these challenges, PPPs remain a popular option for infrastructure development, as they offer a way to leverage private sector expertise and financing to deliver projects on time and within budget. Effective management and risk mitigation strategies can help to address these challenges and ensure successful project delivery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) have become an increasingly popular option for infrastructure development, as they offer a way to leverage private sector expertise and financing to deliver projects on time and within budget. Despite their many benefits, PPPs also come with their own set of challenges, including political and legal risks, complex contract negotiations, limited participation by small firms, and financing challenges.
In summary, the benefits of PPPs in infrastructure development include increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness, transfer of risk, innovation and technology, access to financing, and increased accountability and transparency. Successful examples of PPPs in infrastructure development include the Channel Tunnel (UK-France), the Dulles Greenway (USA), and the Sydney Desalination Plant (Australia). However, PPPs can also face challenges related to financing, contract negotiations, and limited participation by small firms.
Looking to the future, PPPs are likely to continue to play an important role in infrastructure development, particularly in developing countries where there is a significant need for investment in infrastructure. Effective management and risk mitigation strategies can help to address the challenges of PPPs and ensure successful project delivery.