Unveiling the Hidden World: The Intricate Art of Underground Services Installation
The world beneath our feet holds a hidden realm, a labyrinth of intricate networks that power our modern civilization. Unbeknownst to many, the installation of underground services plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth functioning of our cities and communities. From electricity and telecommunication to water and gas, these hidden infrastructures silently serve as the lifelines of our society. In this article, we will explore the art of underground services installation, shedding light on its importance, techniques, challenges, and future possibilities.
Definition of underground services installation
Underground services installation refers to the process of laying and connecting essential utility systems below the ground surface. It involves the installation of various infrastructure components such as pipes, cables, and conduits, which facilitate the transmission of electricity, communication signals, water, sewage, gas, and other vital resources.
Importance of underground services
The installation of underground services is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it helps to minimize visual clutter in urban areas, preserving the aesthetics of our surroundings. By concealing utility networks below ground, we can create cleaner and more appealing cityscapes.
Additionally, underground services offer enhanced reliability and efficiency. Unlike overhead lines and systems, underground installations are less susceptible to external factors such as adverse weather conditions or accidental damage. This ensures uninterrupted service delivery and reduces the risk of power outages, communication disruptions, or water supply failures.
Types of Underground Services
Underground services encompass a wide range of utility systems. Allow us to delve into a selection of prevalent varieties:
Electrical services
Electrical services involve the installation of power cables and transformers to provide electricity to homes, businesses, and public facilities. These systems are designed to handle various voltage levels, ensuring a safe and reliable supply of electrical energy.
Telecommunication services
Telecommunication services comprise the installation of fiber optic cables, telephone lines, and network infrastructure to facilitate voice, data, and internet communication. Underground telecommunication networks are vital for high-speed connectivity and efficient data transmission.
Water and sewage services
Water and sewage services involve the installation of pipes and conduits for the distribution of clean water and the collection and disposal of wastewater. Underground water and sewage networks ensure the availability of clean water and the proper treatment and management of wastewater, contributing to public health and environmental protection.
Gas and oil services
Gas and oil services include the installation of pipelines and storage facilities for the distribution and transportation of natural gas and oil. These underground networks play a crucial role in supplying energy for heating, cooking, and industrial processes.
Cable and fiber optic services
Cable and fiber optic services involve the installation of cables and conduits to transmit audio, video, and data signals. These underground networks support cable television, internet services, and audiovisual communication, enabling seamless connectivity and entertainment options.
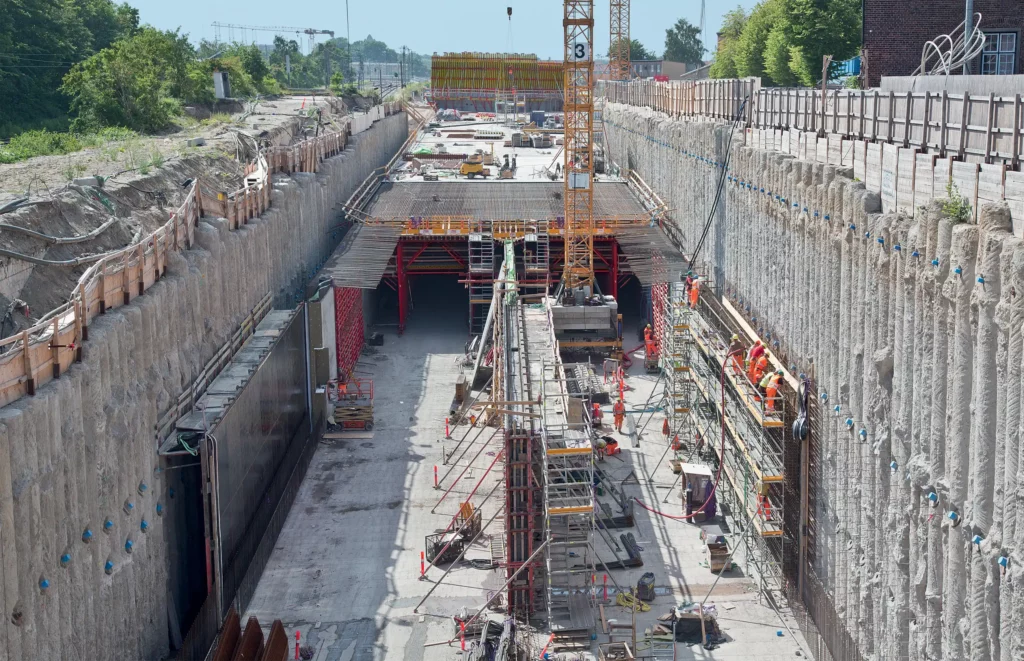
The Art of Underground Services Installation
The installation of underground services is a complex and meticulous process that requires careful planning, skilled labor, and adherence to strict guidelines. Let’s delve into the various stages involved in this artful endeavor:
- Planning and design: Before any installation takes place, thorough planning and design are crucial. This stage involves assessing the requirements of the project, conducting feasibility studies, and creating detailed layouts and blueprints. Factors such as load capacities, route optimization, and future expansion must be considered.
- Excavation and trenching: Excavation and trenching involve the digging of trenches to accommodate the underground infrastructure. Specialized machinery and equipment, such as excavators and trenchers, are used to create precise pathways. Careful attention is given to avoiding existing utilities and maintaining the structural integrity of surrounding infrastructure.
- Pipe laying and conduit installation: Once the trenches are prepared, pipes and conduits are installed. This process involves carefully placing the appropriate materials, such as PVC pipes for water or gas, and conduits for electrical or telecommunication cables. Proper alignment, grading, and joint connections are essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Cable pulling and termination: In the case of telecommunication and electrical installations, cable pulling and termination are critical steps. Cables are carefully pulled through conduits, ensuring they are not stretched or damaged. Termination points, such as connection boxes or cabinets, are installed to facilitate the connection of cables to the main distribution network.
- Testing and commissioning: After installation, comprehensive testing and commissioning procedures are conducted. This involves verifying the functionality and performance of the installed infrastructure, checking for leaks or faults, and ensuring compliance with safety standards. Testing may include pressure tests for water or gas systems, signal testing for telecommunication networks, and insulation resistance checks for electrical installations.
Challenges and Considerations
The art of underground services installation is not without its challenges and considerations. Some key factors to take into account include:
- Utility mapping and identification: One of the primary challenges is accurately mapping and identifying existing underground utilities. This is crucial to avoid damaging or disrupting pre-existing infrastructure during installation. Advanced technologies such as ground-penetrating radar and electromagnetic detectors are employed to identify and locate buried utilities.
- Environmental impact and sustainability: Underground services installation must consider the environmental impact and sustainability aspects. Careful planning and implementation techniques, such as trenchless technology or directional drilling, can minimize disruption to ecosystems, reduce soil erosion, and preserve green spaces. Additionally, sustainable materials and practices are encouraged to minimize the carbon footprint of the installation.
- Safety precautions and regulations: The safety of both workers and the public is of paramount importance during underground services installation. Strict adherence to safety regulations and protocols, such as proper shoring of trenches, use of personal protective equipment, and adequate signage, must be ensured. Regular inspections and risk assessments help mitigate potential hazards and maintain a safe working environment.
- Maintenance and repairs: Regular maintenance and prompt repairs are essential to uphold the functionality and longevity of underground services. Monitoring systems, periodic inspections, and proactive maintenance schedules help identify potential issues and address them promptly. Timely repairs minimize service disruptions and prevent more extensive damage.
Benefits of Underground Services Installation
The intricate art of underground services installation brings forth a multitude of benefits that positively impact our communities and daily lives. Let’s explore some of these advantages:
- Aesthetics and urban development: Underground services eliminate the visual clutter caused by overhead power lines, utility poles, and cables. This enhances the aesthetics of urban areas, creating cleaner and more visually appealing landscapes. Unobstructed views and open spaces contribute to a sense of tranquility and promote urban development.
- Enhanced reliability and efficiency: Underground services offer increased reliability and efficiency compared to their overhead counterparts. Being shielded from external factors such as weather conditions or accidental damage, underground systems are less prone to disruptions. This ensures uninterrupted service delivery, whether it’s a continuous supply of electricity, reliable telecommunication connections, or a steady water and sewage system.
- Long-term cost savings: While the initial installation costs of underground services may be higher than overhead alternatives, the long-term cost savings are significant. Underground infrastructure requires less maintenance, as it is protected from external elements. The reduced need for repairs, replacements, and maintenance activities translates into cost savings over the lifespan of the system.
- Reduced risk of damage and accidents: Underground installation minimizes the risk of damage caused by severe weather events, such as storms or high winds, that can lead to falling trees or objects damaging overhead lines. Additionally, the risk of accidents, such as vehicle collisions with utility poles or contact with live wires, is significantly reduced. This ensures a safer environment for both pedestrians and motorists.
Future Trends and Innovations
The world of underground services installation is constantly evolving, incorporating cutting-edge technologies and innovative approaches. Here are some future trends and possibilities:
- Smart underground infrastructure: The integration of smart technologies in underground services enables real-time monitoring, data analysis, and predictive maintenance. Sensors embedded in pipes, cables, and conduits can detect leaks, faults, or anomalies, allowing for proactive repairs and optimized resource allocation.
- Renewable energy integration: As the demand for renewable energy sources grows, underground services installation will play a vital role in integrating these alternative energy systems. Underground power cables can transmit electricity from solar or wind farms to distribution networks, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting a sustainable energy future.
- IoT and automation: The Internet of Things (IoT) and automation are revolutionizing various industries, and underground services installation is no exception. IoT-enabled devices and automation technologies can streamline installation processes, improve efficiency, and enhance system monitoring and control.
Conclusion
Unveiling the hidden world of underground services installation reveals the intricate artistry and immense importance of this endeavor. From electricity and telecommunication to water and gas, these underground networks form the backbone of modern infrastructure. The careful planning, skilled labor, and adherence to safety standards involved in this process ensure reliable, efficient, and visually appealing urban environments. As we embrace future trends and innovations, the art of underground services installation will continue to shape our cities and pave the way for sustainable and connected communities.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- How long does underground services installation typically take?
Answer: The duration of underground services installation varies depending on the scale and complexity of the project. It can range from a few weeks for smaller residential projects to several months or even years for large-scale infrastructure developments.
- Are there any risks associated with underground services installation?
Answer: While underground services installation minimizes certain risks, there are still potential hazards to consider. These include excavation-related accidents, utility clashes, and unforeseen ground conditions. Adhering to safety regulations and conducting thorough site assessments helps mitigate these risks.
- Can existing underground utilities be damaged during installation?
Answer: With proper planning, mapping, and detection techniques, the risk of damaging existing underground utilities can be minimized. Advanced technologies like ground-penetrating radar and electromagnetic detection devices are used to identify and locate pre-existing infrastructure.
- What happens if repairs are needed on underground services?
Answer: In the event of repairs, underground services can be accessed through access points such as manholes or utility chambers. Specialized equipment and techniques are employed to excavate the affected area, repair or replace the damaged component, and restore the functionality of the system. Prompt repairs help minimize service disruptions.
- Is underground services installation more expensive than overhead installation?
Answer: While the initial installation costs of underground services may be higher than overhead installation, the long-term cost savings often outweigh the upfront expenses. Underground systems require less maintenance and repairs, resulting in lower operational costs over time.
- How does underground services installation contribute to environmental sustainability?
Answer: Underground services installation promotes environmental sustainability in several ways. By minimizing visual clutter, it enhances the aesthetics of urban areas. Additionally, underground systems reduce the risk of damage to trees and vegetation caused by falling objects or tree trimming for overhead lines. Moreover, the integration of smart technologies in underground infrastructure allows for efficient resource management and reduced energy consumption.